XiaoDong Zhang
Dr.Xiaodong Zhang
Ph.D. at Tianjin University (2012) and Postdoc at Stanford University (2015)
Highly Cited Chinese Researcher (2020)
Chief scientist of National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021)
Professor Xiaodong Zhang’s Laboratory has been working on the bioimaging and nanomedicine, including physicochemical design, catalytic mechanism, and treatment of ultra-small cluster molecules in major diseases, NIR-II (1,000-1,700) fluorescence imaging of deep-tissue for pathological monitoring of major diseases, and atomic and molecular design of neural electrodes, interfacial electron transportation and diagnosis and intervention of major diseases.
Xiaodong Zhang’s group has published more than 100 peer-reviewed papers in Nat.Comm., Sci.Adv., Coord.Chem.Rev., Adv.Mater., ACS Nano, and Adv.Funct.Mater. Ten of them have been selected as ESI Highly Cited Papers, and the total number of citations has exceeded 7800 times.

Hao Wang
Hao Wang
In 2012, he graduated from Peking Union Medical College, majoring in radiology
Postdoctoral Fellow at Harvard Medical School(2017-2020)
Join Tianjin University Institute of Medical Engineering and Translational Medicine in 2021
Currently engaged in research in the fields of radiology and biomedical engineering

YongHui Li
YongHui Li
Bachelor of physics, Nankai University (2003-2007)
Doctor of Physics Department of University of Missouri (2007-2014), tutor: Ullrich Carsten
Postdoctoral Fellow of Vanderbilt University (2014-2015), tutor: Kalman Varga
Tianjin University (2016 -)
Main research interests (1) theoretical analysis and Simulation of physical and chemical properties of nano cluster molecules, including photoelectric properties, catalytic properties and process analysis. Prediction and induction of machine learning algorithm for cluster structure. Physical and chemical properties of nano clusters in interstellar medium. (2) Development and application of density functional theory. Including the innovation of algorithm principle, functional innovation, evaluation and comparison. Applications include but are not limited to nanoclusters. (3) The combination of reinforcement learning and quantum system, including the recognition and control of quantum system by artificial intelligence. (4) Evolution and game of complex networks.

LieFeng Feng
1998-2002, Tianjin Normal University, College of physics and electronics, Bachelor
2002-2005, Tianjin University, Department of physics, master, supervisor: Wang Cunda
2005-2008, Tianjin University, Department of physics, doctor, tutor: Jiang enyong, assistant Tutor: Wang Cunda
2008 - present, Department of physics, Tianjin University, work
June 2013-june 2014, University of Washington, USA, studying abroad, young backbone teachers studying abroad
Main research interests: semiconductor light emitting device, laser photoelectric characteristics, semiconductor device physics.

XiaoYu Mu
XiaoYu Mu
Ph.D. at Tianjin University(2018)
Her research work mainly focuses on the design of neural biomaterials, fluorescence imaging in the second infrared region, and its application in the treatment of major neurological diseases.
Xiaoyu Mu has published more than 30 peer-reviewed papers in Sci. Adv. , ACS Nano, Nano Lett., Coord. Chem. Rev., Trends Pharmacol. Sci., Small ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces and other journals. One of them has been selected as ESI Highly Cited Papers, and one has been selected as hot paper.
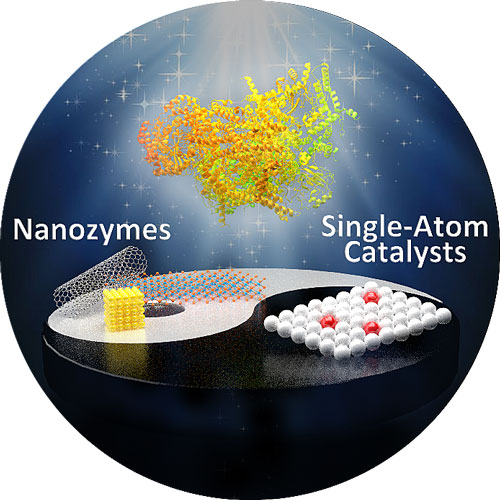
Nanozymes and Single-Atom Catalysts
With the rapid development of nano science, it is found that some nano materials have enzyme like catalytic activity, can catalyze the reaction of natural enzyme substrates, and have a catalytic mechanism similar to natural enzymes. Therefore, they are defined as "nano enzymes". Nano enzyme is a kind of nano materials that can simulate enzyme activity. It not only has the unique physicochemical properties of nano materials, but also has the characteristics of biological enzymes. Compared with natural enzymes, nano enzymes have the characteristics of high catalytic efficiency, good stability, economy and large-scale preparation. Most importantly, due to the inherent characteristics of nano materials, nano enzymes can use mature nanotechnology to control the size and surface modification of materials, so as to regulate their enzyme activity, which not only provides a simple substitute for natural enzymes, but also provides a multi-modal platform connected with complex biological environment
XD.Zhang Lab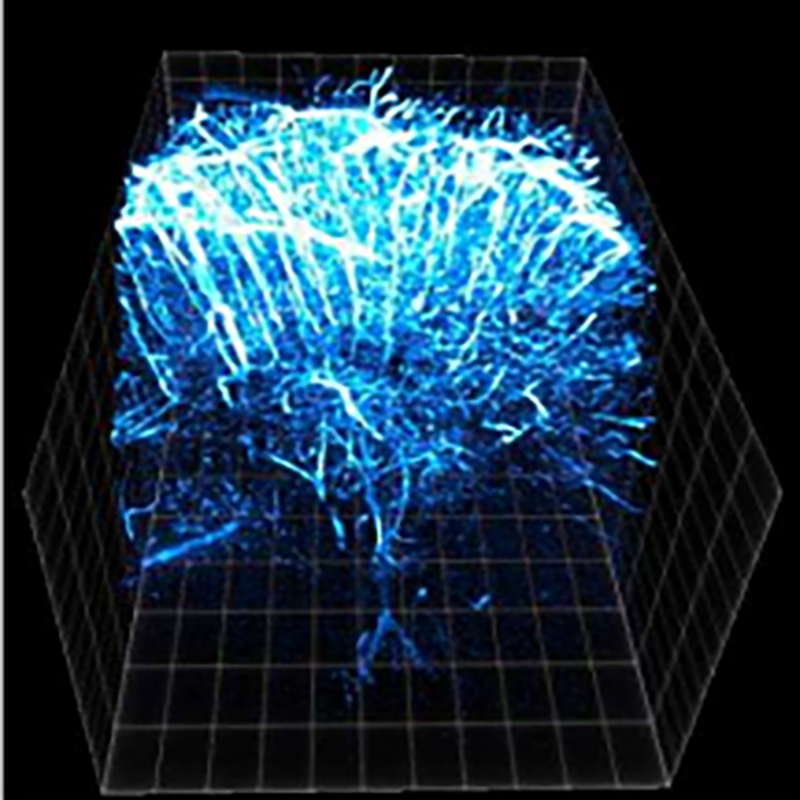
Optical and biological imaging
Biological optical imaging refers to the method of imaging cells, tissues and even organisms by using optical detection means combined with optical detection molecules to obtain biological information. If bio optical imaging is limited to the range of visible light and near-infrared light, according to different detection methods, bio optical imaging can be divided into fluorescence imaging, bioluminescence imaging, photoacoustic imaging, optical tomography and so on. The research direction of our research group is fluorescence imaging in the near-infrared region 2 (1100-1700nm). Within this wavelength range, the scattering of photons in the tissue is small, and the biological self fluorescence can be suppressed to the greatest extent, so as to achieve a deeper penetration depth and obtain images with high signal-to-noise ratio.
XD.Zhang Lab
Biomedicine
Generally, antitumor drugs and biological fluorescent imaging agents need to obtain sufficient animal experimental data before clinical application. Based on the support between the school of science of Tianjin University and the school of medicine of Tianjin University, the team can conduct biological activity tests at the cell and tissue levels and obtain fully accurate experimental results.
XD.Zhang Lab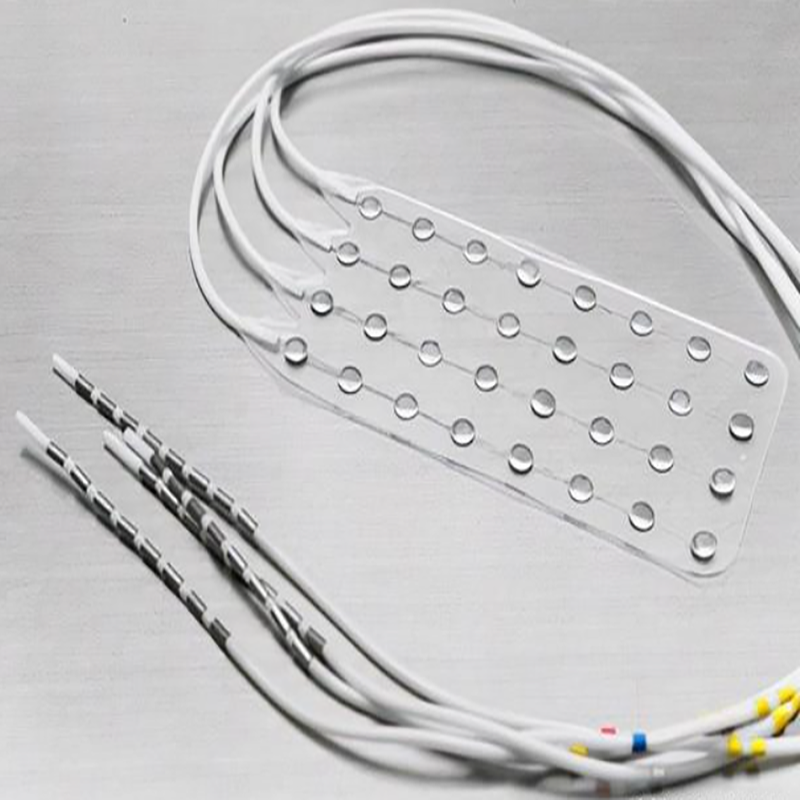
Neural Electrode
Neural electrode can realize two-way electrical signal communication between human tissue and electronic equipment. It is an important part of human-computer fusion and interaction system. At the same time, it also has a broad prospect in restoring and improving human function and nervous system treatment. At present, the common nerve electrodes can be divided into implantable and non implantable. The implantable electrode array can not only record the accurate release time and waveform of neuron action potential in a wide range and with high precision, but also write the information of neurons with high space-time precision. The micro nano processing technology of electrode array, the physical and chemical characteristics of electrode and its interface effect with neural tissue are the important research directions of the front-end of brain computer interface technology, and the important role of new technologies such as nano materials and nano devices in the optimization of neuroelectronic interface is becoming more and more obvious.
XD.Zhang Lab
Our Group
(1) Physicochemical design, catalytic mechanism, and treatment of ultra-small cluster molecules in major diseases (2) NIR-II (1,000-1,700) fluorescence imaging of deep-tissue for pathological monitoring of major diseases (3) Atomic and molecular design of neural electrodes, interfacial electron transportation and diagnosis and intervention of major diseases
XD.Zhang Lab
